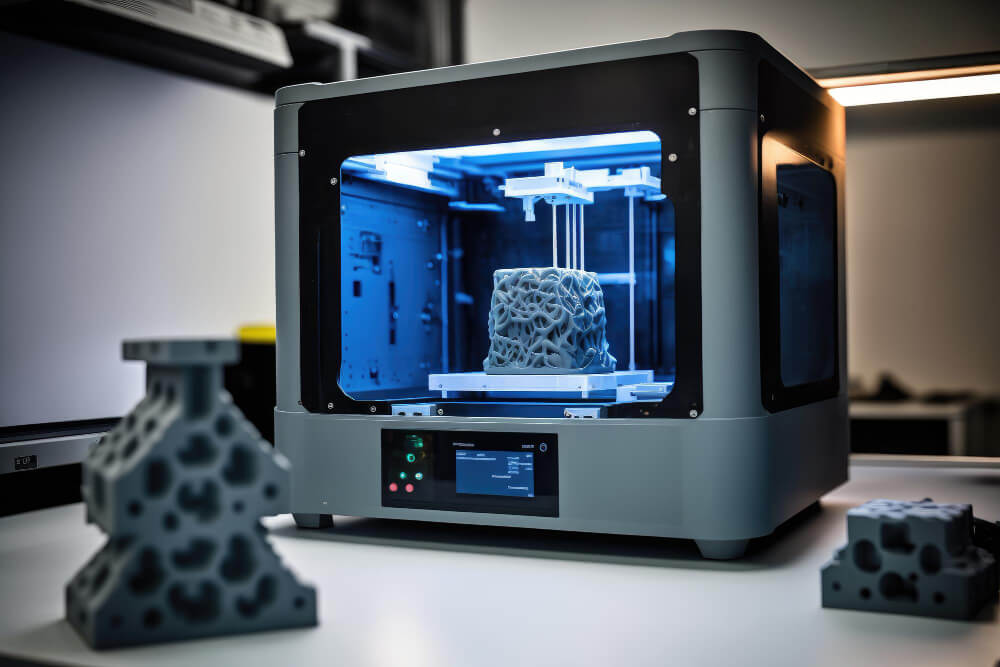
3D printing has made significant advancements in the field of medicine, revolutionizing various aspects of healthcare, including medical device manufacturing, surgical planning, and personalized patient care.
This innovative technology has the potential to transform traditional medical practices and improve patient outcomes.
One of the key applications of 3D printing in medicine is the production of patient-specific anatomical models. These models are created by converting medical imaging data, such as CT or MRI scans, into highly accurate 3D representations. Surgeons and healthcare professionals can then use these models to visualize complex anatomical structures, plan surgical procedures, and improve preoperative training. This enhanced visualization and hands-on experience can lead to more precise surgeries, reduced operating times, and improved patient safety.

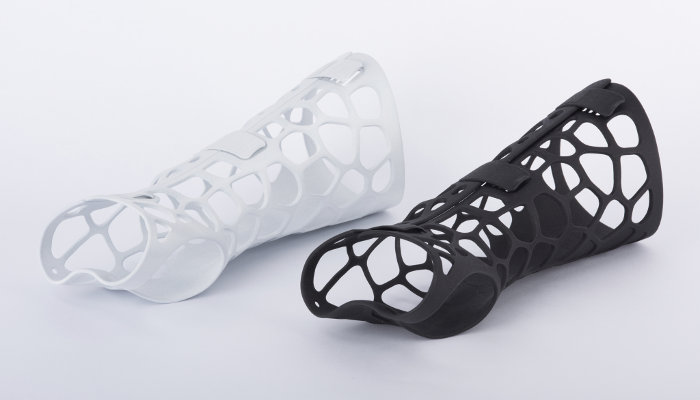
In addition to anatomical models, 3D printing enables the fabrication of patient-specific implants and prosthetics. By using 3D scanning and printing technologies, customized implants and prosthetic devices can be designed and manufactured to fit a patient’s unique anatomy. This personalization improves the functionality, comfort, and aesthetics of the devices, enhancing patient mobility and quality of life.