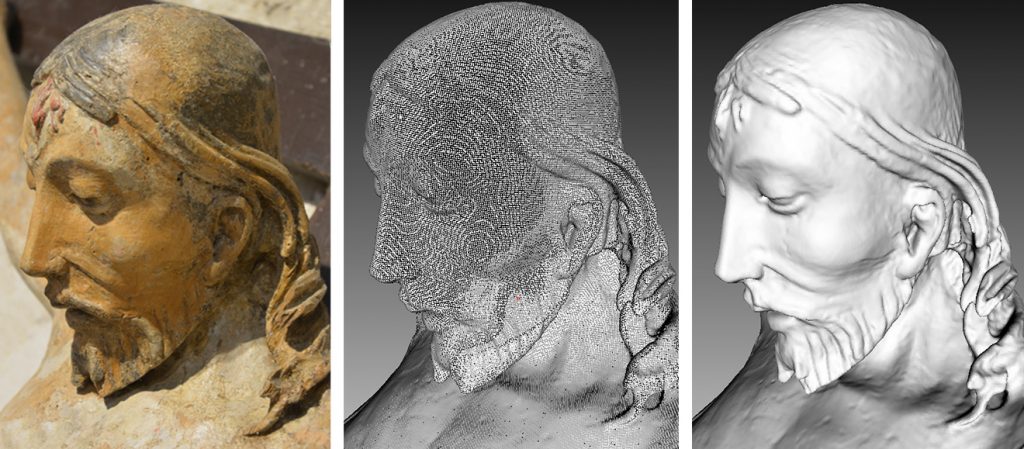
Digitization of an existing part
Reversible engineering is the digitization of an existing part, assembly, or product that does not have technical documentation or a CAD model. It is also defined as the process of obtaining a CAD model from spatial points obtained by digitization (scanning or similar processes) of an actual part or product. It is used in various fields of science and technology, such as manufacturing, product development, and design, medicine, architecture, archeology and in many other segments that require digitization of real parts. When it comes to developing new products, reversible engineering has a significant role to play in accelerating this process.

One of the primary applications of reverse engineering is in product development and innovation. By studying and analyzing existing products, engineers and designers can understand their underlying principles and use that knowledge to create improved versions or entirely new products. This is especially valuable when the original design documentation is unavailable or incomplete.
Reverse engineering also plays a crucial role in maintenance, repair, and replacement of parts. When components become obsolete, damaged, or no longer available, reverse engineering can help recreate those parts, ensuring the continued functionality of the system or equipment.